Setting the language for dashboards, datasets and the app
When you started dashboarding, you may have noticed that our application and charts are set to English by default. For example, the dates are written in English, you see a 'deselect all' button in the dynamic filters and when there is data missing, you see a category named 'other'.
But don’t you worry, English is not the only language our smart tool speaks. In fact, you can have your dashboard in almost every language you wish for.
This article covers:
- Changing your application language and default dashboard language
- Adding a dataset language
- Translate column names to inform tooltips and legends
- Add translations for your textual data
- Define the default format of columns
- Adding a dashboard language
- Allows you to translate elements such as titles, tooltips, ...
- Ensures automatic translation of auto-generated text such month names as in the date filter.
- Informs Locale-Aware Formatting for Dates and Numbers
Changing your application language and default dashboard language
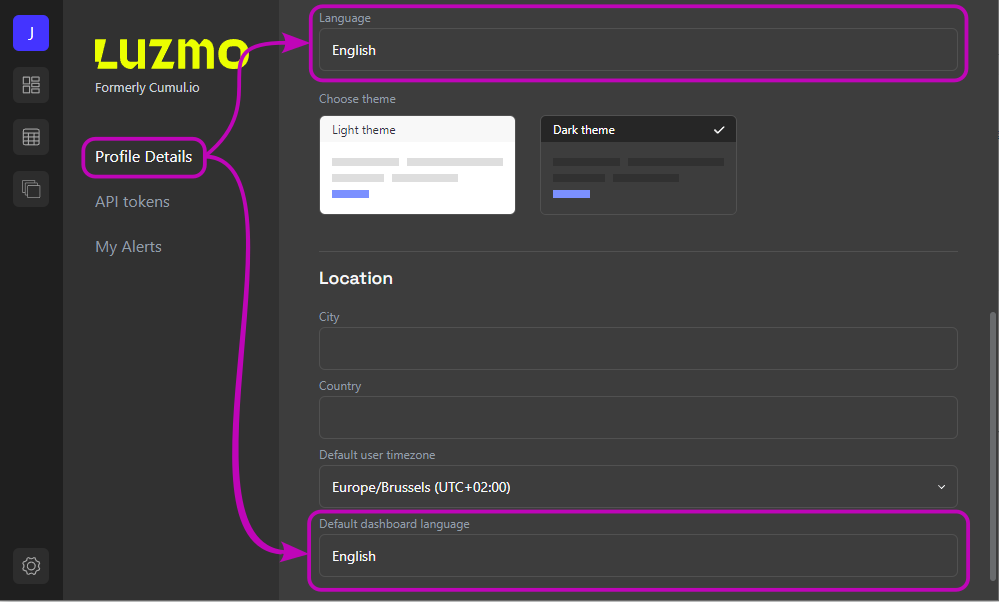
In the "Profile details" section of the profile menu you can set your application language and default dashboard language.
The application language will change the language of the Luzmo user interface. Whereas the default dashboard language determines the language to which a newly created dashboard will be set.
Adding a dataset language
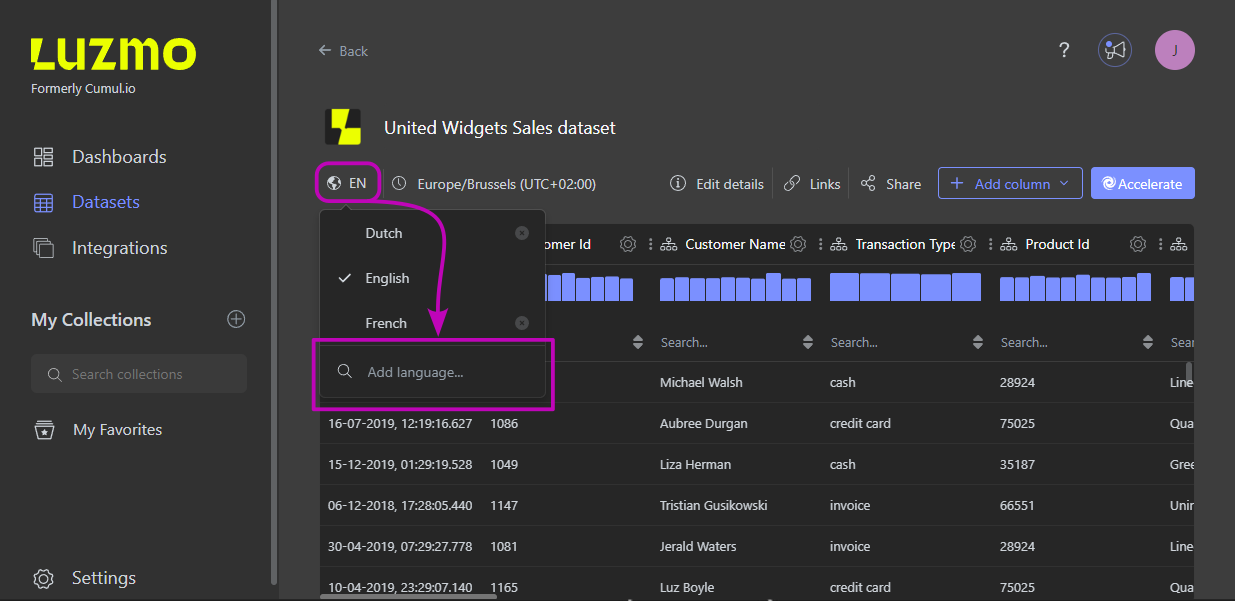
You can also set up languages for your datasets. You can see the currently configured language next to the globe icon on the databoard. By following the same steps as in the dashboard (search and select), you can add extra languages.
Column names
The column names, which are used for the labels and legends in charts can be modified per chart in a dashboard or ideally directly on the dataset to set its default value. The recommended approach is to ensure you add the different languages and translated column names to your dataset as a first step, and as a second step build your dashboards using these. The labels in dashboards build before adding the translations to the datasets will not be changed.
Add translations for your textual data
Add translations in Luzmo
After adding languages to your dataset (see above), the hierarchy editor may be used to specify the translated labels to display instead of the original value. The changes will be reflected when the dataset is used on a dashboard using that language (see Adding a dashboard language).
If you have a lot of translations that need to be added, you can also set up these translations using the Luzmo API.
Provide translated values from the data source
It may be preffered to provide the translated values from the datasource in case these are available there.
Option 1: different datasource per language - In case you have have a different data source for each language, you can use account overrides to change the dataset queried based on the language each user should see. For more information on account overrides refer to the academy article regarding Multi-tenancy by overriding data source properties
Option 2: different rows per language in 1 dataset - In case you have the translated information replicated into several rows, meaning you have one row for each language and a column that specifies the language that row of that is in, you can filter the information through a parameter filter set when authenticating your users. More information about this can be found on our article regarding Multi-tenancy by using parameter filters
Option 3: column per language in 1 dataset - In case you have a column per language and your data source is an SQL database, you can use parameterized SQL datasets to change the column queried depeding on the user's language as explained in the Parameterized SQL datasets section of the article on SQL datasets.
For example, the table in your database would contain language specific columns with names such as "NL Age group", "EN Age group", and "FR Age group". After connecting your data source using our connectors, you can use SQL datasets to create a dataset as follows:
SELECT
id,
value,
.... -- select columns as needed
'{{metadata.age_group_column_name|EN Age group}}' AS "Age group" -- parameterized SQL format: {{parameter_name|default_value}}
FROM
table
In your backend's embed authorization request you override the parameters defined in your SQL datasets to dynamically point towards the column containing the selected language's translations. For example, specify the following metadata in the embed authorization request to show French data:
"metadata": {
"age_group_column_name": "FR Age group"
}
or
SELECT
id,
value,
.... // select columns as needed
CASE
WHEN {{metadata.language|Dutch}} = 'Dutch' THEN 'NL Age group' -- parameterized SQL format: {{parameter_name|default_value}}
WHEN {{metadata.language|Dutch}} = 'French' THEN 'FR Age group'
WHEN {{metadata.language|Dutch}} = 'English' THEN 'EN Age group'
ELSE 'NL Age group'
END category -- CASE switcher statement to select correct column based on language parameter
FROM
table
In your backend's embed authorization request you override the parameters defined in your SQL datasets to specify the selected language. For example, specify the following metadata in the embed authorization request to show French data:
"metadata": {
"language": "French"
}
Option 4: custom logic via Plugin - A Plugin can also be used so that different data may be presented to each user based on their language. Information on multitenancy via plugin can be found here
In this case you can add in the metadata property of the embed token the language in which you want the values to appear. This metadata will be present in the request for data to your plugin. As such you can use this information to ensure the data is returned in the desired language.
For example, specify the following metadata in the embed authorization request to show French data:
"metadata": {
"language": "French"
}
Define the default format of columns
If you like the format of your numbers and dates to be locale-aware by default, you can set the default format to "auto" via the column settings in the databoard. More info here on how to set the default format.
Adding a dashboard language
Each dashboard can have multiple languages enabled. You can instantly see in which language the dashboard is set by clicking on the globe icon. For each new dashboard you create, this will automatically be set to your "default dashboard language" which you set in your Profile.
To add extra languages: click the globe icon, search for your language of choice, click it to select. You can now toggle between the different languages.
"Automatic text" such as dates, "select all", etc will be automatically translated to your chosen language.
Chart titles are to your discretion to translate. When it comes to the data displayed in the charts, you can translate these by adding languages to your dataset (see above).

Locale-Aware Formatting for Dates and Numbers
Luzmo supports locale-aware formatting for numbers and dates to enhance the readability of your dashboards. When you select the 'auto' option in the slot menu, numbers and dates automatically format based on the current dashboard language.
Numbers: Decimal and thousands separators adjust based on language. For example, English employs a comma as the thousand separator, whereas Dutch uses a period.
Dates: Formats adapt to mmdd or ddmm based on language, with the appropriate separator between day, month, and year. For example, US English uses "04/15/2022" as the date format, while Dutch uses "15-04-2022."
You can still opt for fixed formats that remain consistent across dashboard languages.